What Is DIPG?
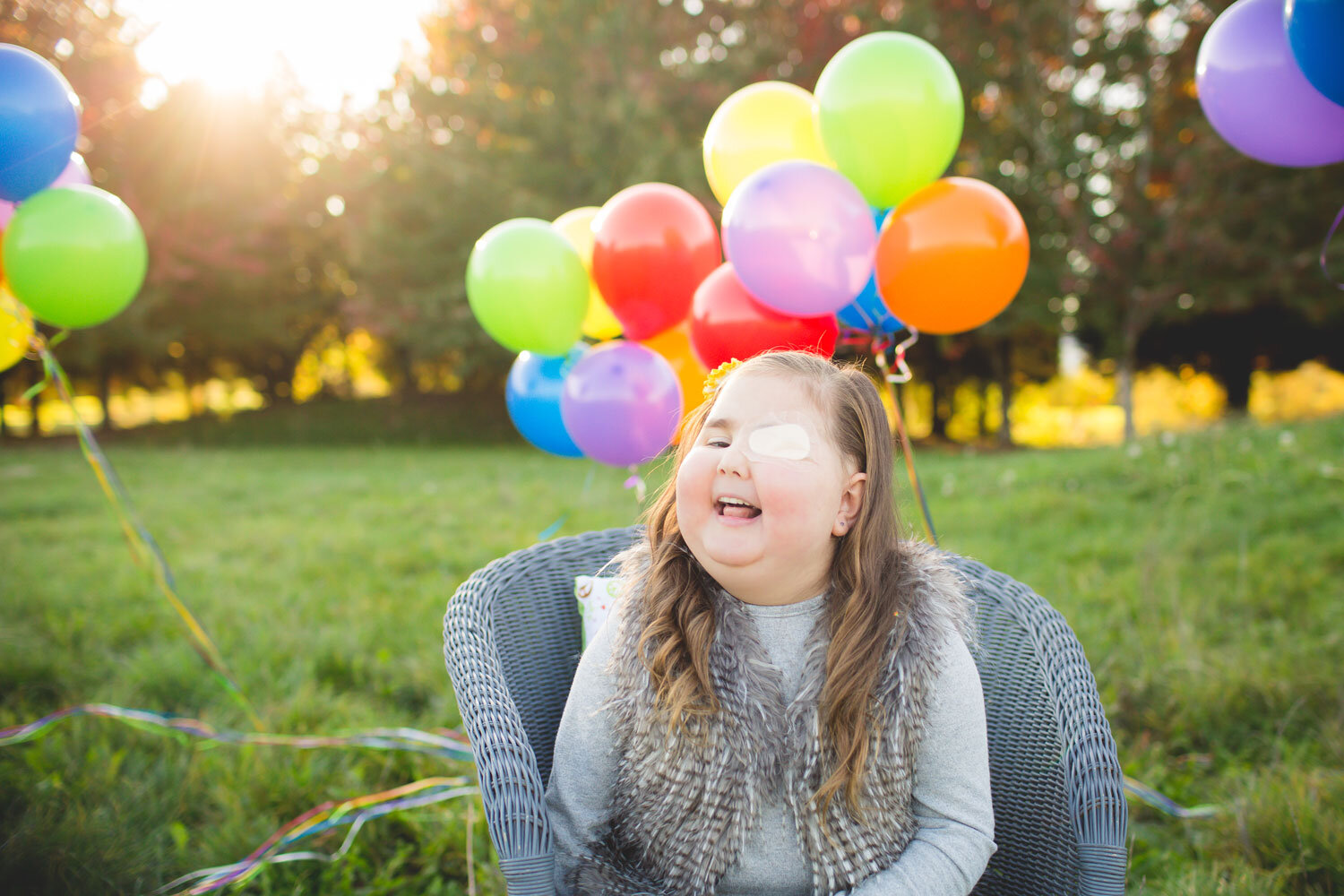
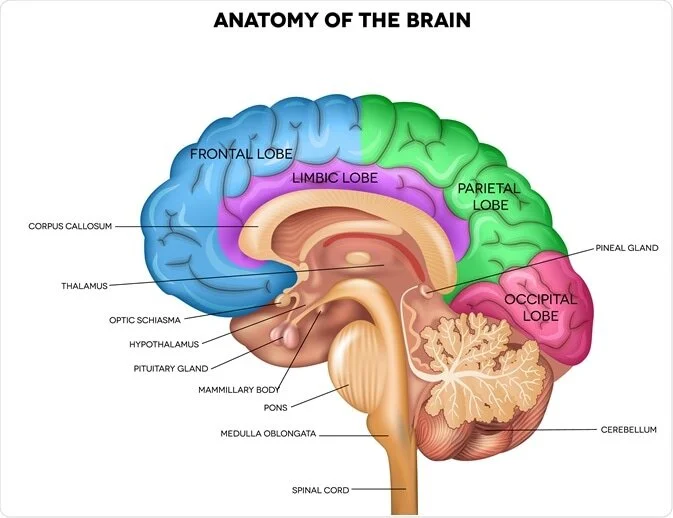
What is DIPG? Diffuse Intrinsic Pontine Glioma, commonly referred to as pontine glioma, infiltrative brainstem glioma, or DIPG, is a rare terminal tumor of the brainstem that occurs almost exclusively in children.
Image Credit: Tefi/Shutterstock.com
A pontine glioma occurs in the most delicate area of the brainstem (the pons), which controls many critical functions, including breathing and blood pressure. Its location, as well as the way it infiltrates normal brain tissue, makes it especially difficult to treat.
There are about 300-350 new cases of DIPG diagnosed each year in the United States alone, usually in children under the age of 10. More than 90 percent of children diagnosed with DIPG will die within 2 years of diagnosis, and most children will live only 9 months.
To make matters worse, these last few months of the child’s life are excruciatingly difficult as the tumor interferes with essential bodily functions like breathing, swallowing, eye movement, and balance. Most children with DIPG develop double vision and lose the ability to walk, talk, eat and drink.